Certification Classroom | Seven Very Important Quality Management Terms
Release Date:
2020-09-28 16:33
Source:
Today, let's learn about seven very important quality management professional terms.

Specialized Terms in Quality Management
1. Quality Policy
Quality policy is the overall quality purpose and direction formally issued by the top management of an organization. The quality policy of an enterprise (sometimes also called quality policy) is the action guideline that all departments and personnel of the enterprise must follow and comply with when performing quality functions and engaging in quality management activities. Different enterprises can have different quality policies, but they must all have clear appeal. Quality policies such as "Survive by quality, develop by products," "Quality first, service first," and "Surpass the world's or industry's advanced level" are suitable for external promotion of enterprises because they are a highly summarized and strongly appealing expression of the enterprise's quality policy. However, for internal guidance within the enterprise, such descriptions and summaries are too general and need to be clarified and made specific.
2. Quality Objectives
The definition of quality objectives is: "The goals pursued in terms of quality." From the theory of quality management, the theoretical basis of quality objectives is behavioral science and systems theory. The famous Western philosopher Maslow (A.B. Maslow) proposed the "Hierarchy of Needs" theory, which divides human needs into layers: physiological needs, safety needs, belonging and love needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs. He believed that when a person's physiological and safety needs are well satisfied, their focus gradually shifts to higher-level needs such as belonging and love, esteem, and self-actualization. At this point, as employees of an enterprise, they hope to be recognized and accepted by the enterprise, to be competent in their work and achieve accomplishments, to receive high evaluation from others and the enterprise, gain certain reputation and achievements, and even reach the realm of self-expression and fulfillment. Therefore, as top management and managers of the enterprise, to motivate and stimulate employees' creativity and enthusiasm, it is necessary to guide all employees to satisfy their higher-level needs through the successful realization of their own quality objectives.
Quality objectives are based on the "motivation theory" in behavioral science but also develop forward with the help of systems theory. According to systems theory, an enterprise is a purposeful system that includes several purposeful subsystems, which in turn include purposeful sub-subsystems, and so on infinitely. Guided by systems thinking, starting from achieving the overall quality objectives of the enterprise, coordinating the activities of all departments and even every individual is the core idea of quality objectives.
3. Quality System
With the development of science and technology, product structures have become increasingly complex, and users and consumers have higher demands for product quality, especially for product reliability and safety. Coupled with frequent international trade and increased trade volume, a series of international issues such as product quality disputes and product quality liability inevitably arise. To ensure product quality and promote and guide enterprises to improve quality management levels, the International Organization for Standardization officially released the ISO9000 series of quality management and quality assurance standards in 1987. China adopted these standards equivalently in 1988 and formally adopted the GB/T19000 series standards on January 1, 1993, to promote the improvement of producers' quality management levels and quality assurance capabilities and to adapt to the development needs of international trade.
A quality system refers to the organizational structure, procedures, processes, and resources implemented for quality management.
4. Quality Control
Quality control refers to the operational techniques and activities taken to meet quality requirements. This means that quality control aims to monitor the quality formation process and eliminate factors causing nonconformity or unsatisfactory effects at all stages of the quality chain. The goal is to meet quality requirements and obtain economic benefits through various quality operation techniques and activities. In the enterprise field, quality control activities mainly involve internal production site management. It is unrelated to whether there is a contract and refers to technical and management measures taken to achieve and maintain quality. Quality inspection is subordinate to quality control and is an important activity of quality control.
Steps of Quality Control
1. Establish standards. Determine the quality standards required for the product's cost, performance, safety, reliability, etc.
2. Evaluate the degree of conformity to the standards.
3. Take measures when necessary. Take measures on various factors affecting user satisfaction such as marketing, design, engineering, production, and maintenance to solve problems.
4. Develop improvement plans. Develop plans to reduce costs and improve performance, safety, and reliability standards.
5. Quality Assurance
Quality assurance refers to all planned and systematic activities implemented within the quality system and verified as needed to assure people that an entity can meet quality requirements. Obviously, quality assurance generally applies to contractual situations, and its main purpose is to assure users that products or services meet specified quality requirements. If the given quality requirements do not fully reflect user needs, quality assurance cannot be perfect.
Quality assurance is divided into internal quality assurance and external quality assurance. Internal quality assurance is a management tool within the enterprise aimed at gaining the trust of enterprise leadership. External quality assurance is a means for the supplier to gain the trust of the buyer in a contractual environment. Therefore, the content of quality assurance is not simply to guarantee quality but more importantly to provide sufficient and reliable evidence through a series of planned and organized evaluation activities of the quality system elements affecting quality to gain the trust of enterprise leadership and buyers.
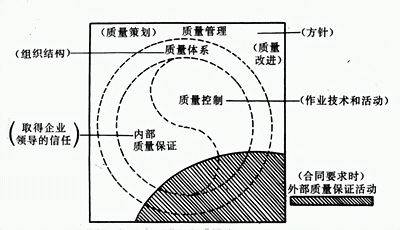
Of course, quality assurance is based on quality control; without quality control, there is no quality assurance. Sometimes, quality control activities and quality assurance activities are related (see the figure below).
 Click to add image description (up to 60 characters) Edit
Click to add image description (up to 60 characters) Edit
In the above figure, the square represents all quality management work. To carry out quality management, the quality policy should first be formulated, along with quality planning, design, and the establishment of a scientific and effective quality system. To establish a quality system, a quality management organization should be set up with clear responsibilities and authorities, followed by quality control activities and internal quality assurance activities. Quality control activities are operational techniques and activities, while internal quality assurance activities are carried out to gain the trust of enterprise leadership. The two are separated by a dashed S-shape, indicating that these two activities are difficult to distinguish clearly. The small dashed circles indicate that the activities and work within the square are all quality management. Using solid circles would separate them from quality management.
The arc-shaped slanted line part represents external quality assurance activities, which occur only when there are quality assurance requirements in contracts or regulations. The implementation of these external quality assurance activities aims to gain the trust of the buyer. The arc-shaped part covering the square vividly illustrates that external quality assurance can only be established on the basis of internal enterprise quality management. In other words, the quality assurance system should be built on the quality management system. Without quality management and quality control, there is no quality assurance. Without a quality management system, it is impossible to establish a quality assurance system.
Through quality control and quality assurance activities, weak links and existing problems in quality work are identified, and targeted quality improvement measures are taken, entering a new round of the quality management PDCA cycle to continuously achieve quality management effectiveness.
6. Quality Planning
Quality planning is part of quality management, dedicated to setting quality objectives and specifying the necessary operational processes and related resources to achieve the quality objectives.
Quality management is the guidance and control of activities related to quality, usually including the establishment of quality policies and quality objectives, quality planning, quality control, quality assurance, and quality improvement. Obviously, quality planning belongs to the "guidance" of quality-related activities, that is, it "guides" quality control, quality assurance, and quality improvement activities. In quality management, the status of quality planning is lower than the establishment of quality policies, which is the premise for setting quality objectives, and higher than quality control, quality assurance, and quality improvement. Quality control, quality assurance, and quality improvement can only have clear objects and goals, as well as practical measures and methods, after quality planning. Therefore, quality planning is an indispensable intermediate link among many quality management activities, serving as a bridge and link between quality policies (which may be "virtual" or "soft" quality management activities) and specific quality management activities (often regarded as "real" or "hard" work).
7. Quality Plan
The definition of "Quality Plan" is: "A document specifying special quality measures, resources, and the sequence of activities for a specific product, project, or contract."
Definition Explanation
1. The object of quality plan preparation is a specific product, project, or contract.
2. The content of the quality plan should specify special quality measures, resources, and the sequence of activities.
3. The quality plan should be consistent with the requirements of the quality manual and may refer to relevant parts of the manual applicable to specific situations.
4. The quality plan should be documented in writing and is part of the quality system documents.
5. The quality plan is usually a result of "quality planning." It is a document for a specific object and is an "activity to determine quality and the objectives and requirements for using quality system elements."
Content of the Quality Plan
1. Clarify its scope and purpose (applicable products, projects; special requirements and validity period) and the quality objectives to be achieved;
2. Steps of each process in actual operation (process requirements can be shown using flowcharts or similar diagrams);
3. Specific allocation of related responsibilities, authorities, and resources at different stages of the project;
4. Specific documented procedures and instructions adopted;
5. Inspection, testing, checking, and audit outlines applicable at appropriate stages;
6. Documented procedures for modifying and improving the quality plan as the project progresses;
7. Measurement methods to achieve quality objectives and the measures taken.
About Beijing United Intelligence Certification Co., Ltd.
Beijing United Intelligence Certification Co., Ltd. (abbreviated as UICC) is an important member unit of Beijing United Intelligence Technology Group. It is an international and comprehensive standard certification and evaluation technical service organization. The company provides intellectual services for nearly all industry customers worldwide in standardized development, informatization development, green development, innovative technology development, and carries out standard certification, review and evaluation, standard research and development, technological innovation, green ecological development, environmental protection and energy-saving technology, quality management technology, safety production technology, informatization technology, information system development, professional training, policy compliance, technology promotion, and other high-tech services.
The company has been established for more than 20 years, with a wide range of business and rich experience. It has set up more than 20 branches nationwide, providing convenient and fast customer service. It has provided certification/review/evaluation, innovation/development/research, application/promotion/training, and other technical services to more than 50,000 customers, issuing a total of more than 100,000 certificates.
Related News
Related Downloads
Related News
undefined


